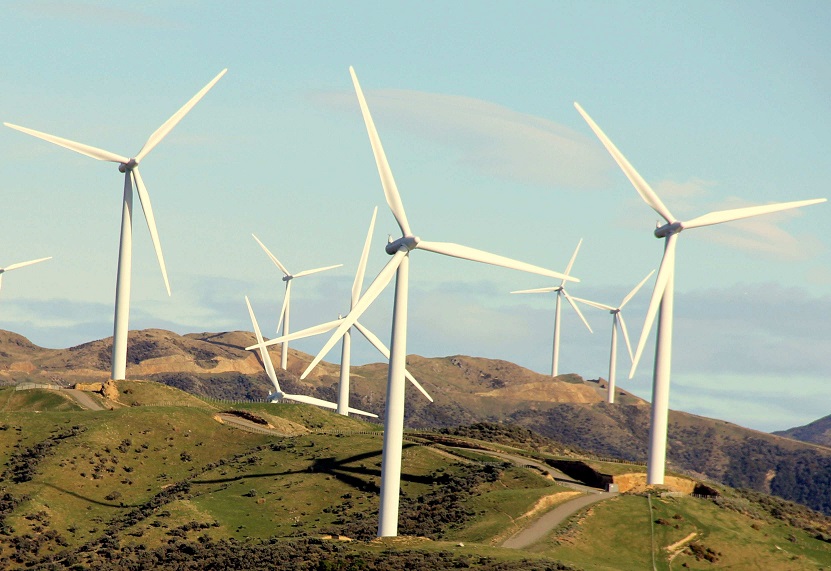
SCADA Miner generated this exception report when the wind turbine reactive power output was unable to meet its requested set-point.
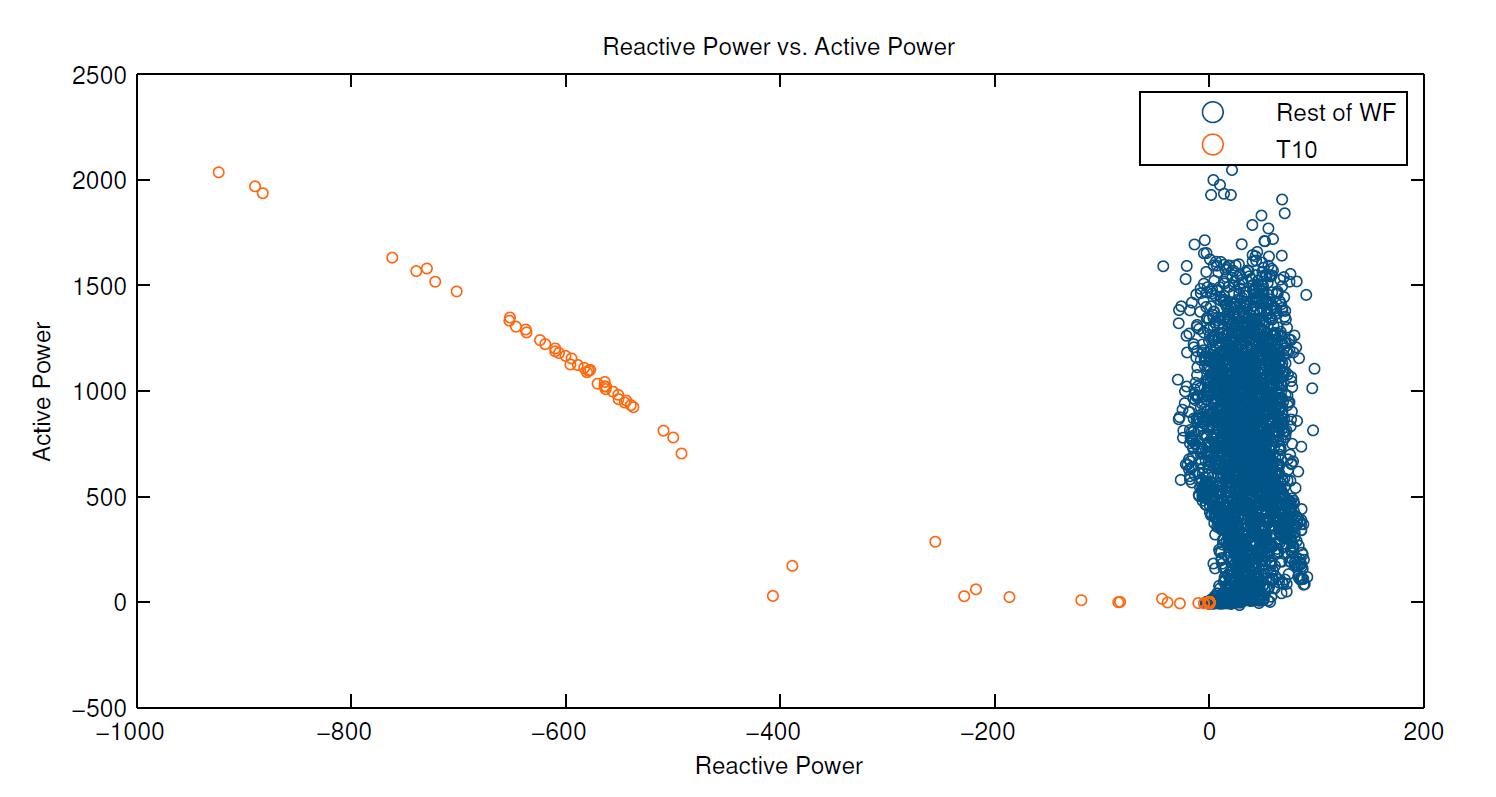 Turbine 10 is consuming reactive power as active power increases. While this can cause compliance issues, there are also other side effects.
Turbine 10 is consuming reactive power as active power increases. While this can cause compliance issues, there are also other side effects.
Additional loading on the medium voltage reticulation system.
The wind farm designers may have sized the medium voltage distribution network to carry the full wind farm load under the assumed operating conditions of unity power factor at the wind turbine terminals. If multiple wind turbines are failing to meet their reactive power targets then in extreme cases this can overload the medium voltage reticulation and cause cable joint failures, resulting in significant downtime and lost production.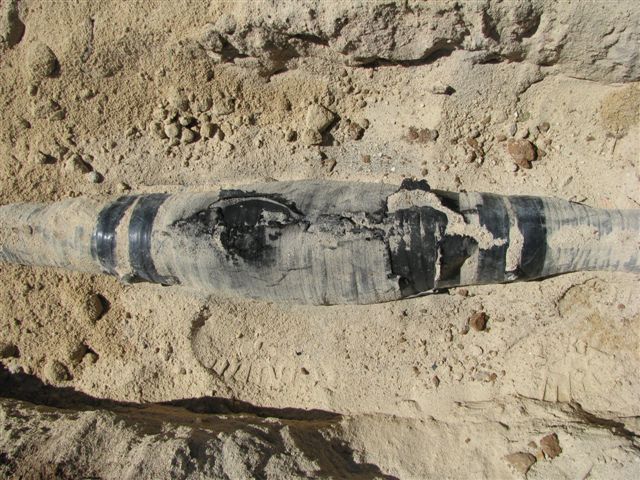 Wind farm MV cable joint failures can occur due to overloading if the wind turbines are not operating within their intended reactive power limits.
Wind farm MV cable joint failures can occur due to overloading if the wind turbines are not operating within their intended reactive power limits.
Increased Duty on substation reactive compensation system (if installed)
In order to maintain compliance at the point of common coupling, the substation reactive plant may see increased duty. These systems (such as the AMSC DVAR or S&C DSTATCOM, or even a utility scale battery) are best reserved for providing rapid reactive support during grid voltage dips rather than providing steady state reactive support. Refer to our article on optimal wind farm voltage control.
Higher real power losses (lost revenue)
Due to sub-optimal load flow conditions on the wind farm, increased reactive current can increase I2R losses within the wind farm.
A turbine manufacturer is not likely to alert a wind farm owner to such problems because:
- It is not incentivised to do so under availability contracts
- The wind turbine OEM may have to spend money to fix the problem
- The problem doesn’t have an immediate effect on availability.
Because reactive power issues don’t usually impact availability, they can go unnoticed for long periods of time. SCADA Miner regularly performs checks of reactive power at the turbine terminals as well as the point of common coupling. SCADA Miner generates exception reports if conditions require attention.